Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, is a surgical technique that uses small incisions and specialized surgical tools to access and operate on internal organs. Instead of making a large incision, several small incisions are made in the abdomen or pelvis, and a laparoscope, which is a thin, lighted tube with a camera, is inserted through one of the incisions to guide the surgical instruments.
The benefits of laparoscopic surgery over traditional open surgery include reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and smaller scars. Laparoscopic surgery can be used for a variety of procedures, including gallbladder removal, appendectomy, hernia repair, and hysterectomy.
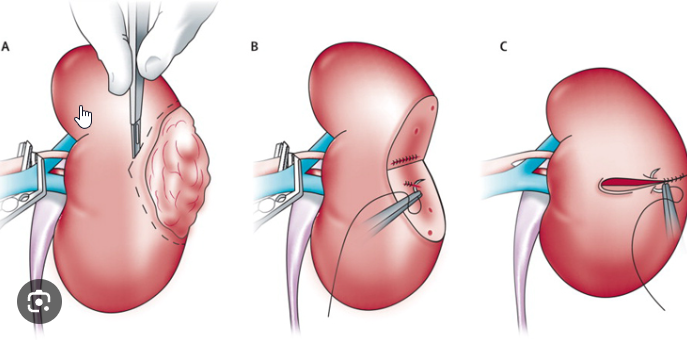
Nephrectomy
Nephrectomy is a surgical procedure to remove all or part of a kidney. It is usually recommended when a kidney is damaged or diseased, such as in the case of kidney cancer, severe infection, or significant injury. A nephrectomy may be performed using open surgery or minimally invasive techniques such as laparoscopy or robotic surgery.
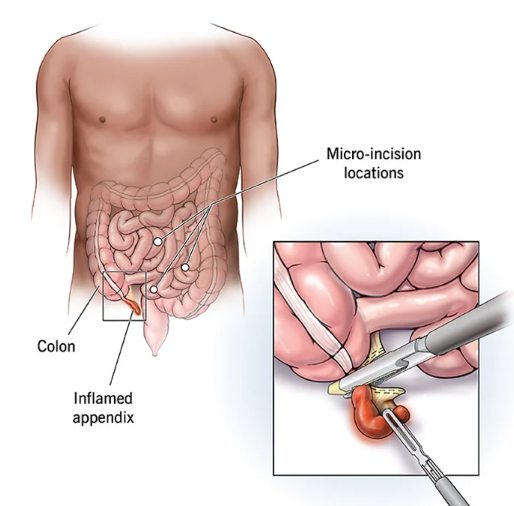
Appendectomy
An appendectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the appendix. The appendix is a small, finger-shaped pouch that is attached to the large intestine. Appendectomy is usually performed when the appendix becomes inflamed and infected, a condition known as appendicitis.
Appendectomy can be performed using open surgery or laparoscopic surgery. In open surgery, the surgeon makes a single incision in the lower right side of the abdomen to remove the appendix. In laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdomen and inserts a laparoscope and surgical instruments to remove the appendix.
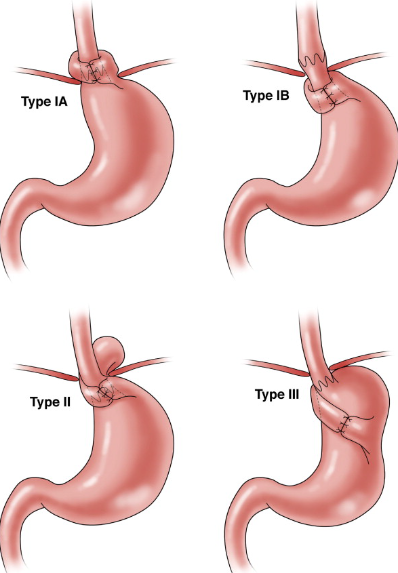
Fundoplication
Fundoplication is a surgical procedure used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). GERD is a condition in which stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing heartburn, chest pain, and other symptoms. Fundoplication surgery aims to prevent the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus by strengthening the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which is the muscle that separates the esophagus from the stomach.
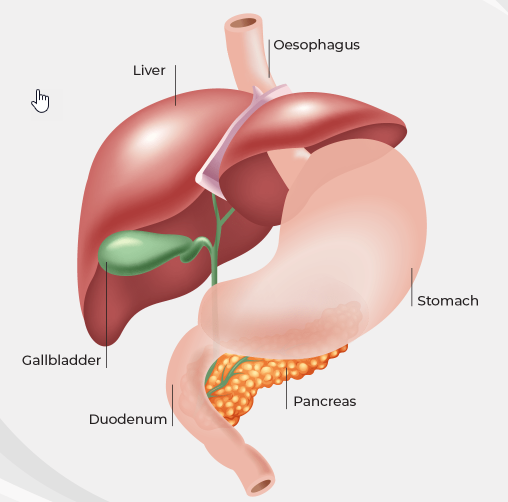
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small organ located under the liver that stores bile, a digestive fluid that helps break down fats in the small intestine. Cholecystectomy is typically performed when gallstones or other problems with the gallbladder cause pain, inflammation, or infection.
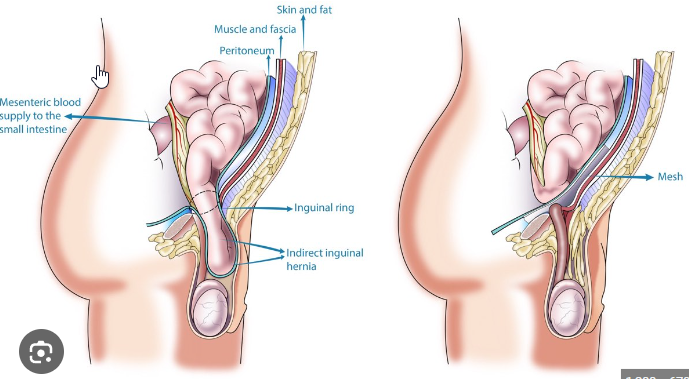
Hernia Surgery
Hernia surgery is a surgical procedure to repair a hernia, which is a bulging of an organ or tissue through a weakened area of muscle or connective tissue. Hernias can occur in different parts of the body, but most commonly occur in the abdominal area, groin, or upper thigh.
There are two main types of hernia surgery: open surgery and laparoscopic surgery. In open surgery, the surgeon makes an incision near the hernia and pushes the bulging tissue back into place. The weakened area of muscle or connective tissue is then reinforced with a mesh patch.