Prostate
The prostate is a small gland located in the male reproductive system. It is situated just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, which is the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. The main function of the prostate is to produce and secrete fluid that makes up a part of semen. This fluid helps to nourish and protect the sperm that are ejaculated during sexual intercourse.
The prostate can sometimes become enlarged, which can cause urinary problems such as difficulty starting or stopping urination, a weak urine stream, or a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Enlargement of the prostate is a common condition that typically occurs as men age. In some cases, an enlarged prostate can be a sign of prostate cancer, which is a serious condition that requires medical attention.
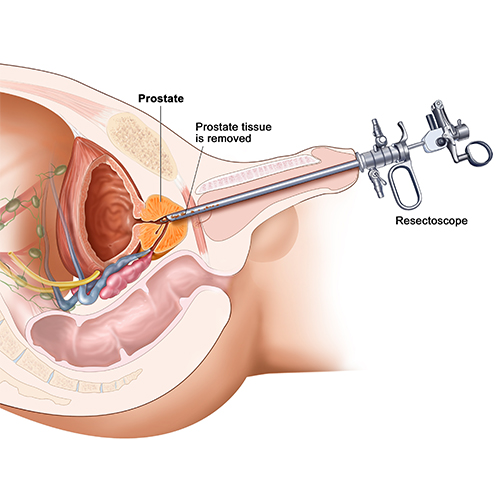
Monopolar TURP
Monopolar Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) is a surgical procedure used to treat an enlarged prostate gland. In this procedure, a small wire loop is inserted through the urethra and into the prostate gland. An electrical current is then passed through the wire loop, which is used to remove small pieces of tissue from the prostate gland.
The monopolar TURP procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and may require a short hospital stay. It is considered to be a safe and effective treatment for relieving the symptoms of an enlarged prostate, such as difficulty urinating, frequent urination, and urinary urgency.
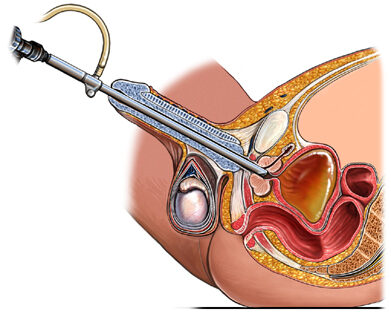
Cardiac Safe Bipolar TURP
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a common surgical procedure used to treat urinary symptoms caused by an enlarged prostate gland. Bipolar TURP is a modification of the traditional monopolar TURP technique that uses a different energy source to remove tissue from the prostate.
Cardiac safety is an important consideration for any surgical procedure, as some patients with underlying heart conditions may be at increased risk of complications during and after surgery. With that said, bipolar TURP is generally considered to be a safer option than monopolar TURP in terms of cardiac safety.
One of the reasons for this is that bipolar TURP uses lower energy levels, which can lead to less bleeding and tissue damage. This, in turn, can result in a lower risk of fluid absorption and electrolyte imbalances, which are potential complications that can impact cardiac function.
